Home /
Expert Answers /
Accounting /
what-are-the-eight-parts-of-a-standard-unmodified-opinion-audit-report-for-a-nonpublic-entity-and-w-pa786
(Solved): What are the eight parts of a standard unmodified opinion audit report for a nonpublic entity and w ...
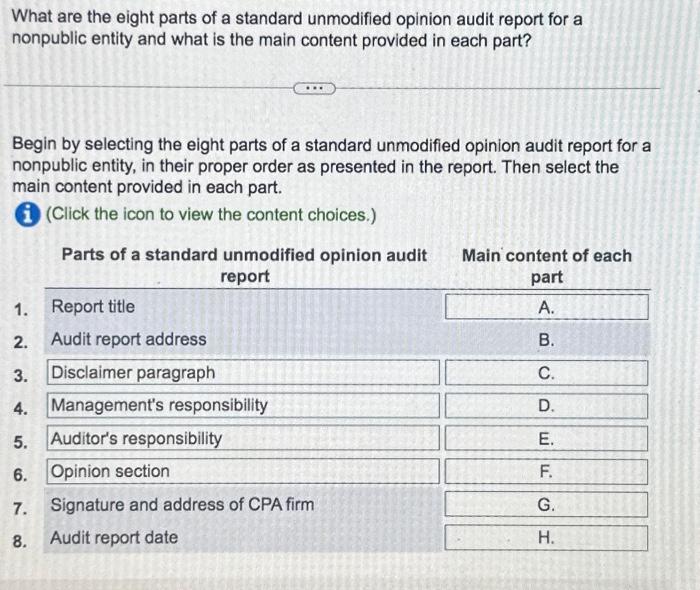
What are the eight parts of a standard unmodified opinion audit report for a nonpublic entity and what is the main content provided in each part? Begin by selecting the eight parts of a standard unmodified opinion audit report for a nonpublic entity, in their proper order as presented in the report. Then select the main content provided in each part. (Click the icon to view the content choices.)
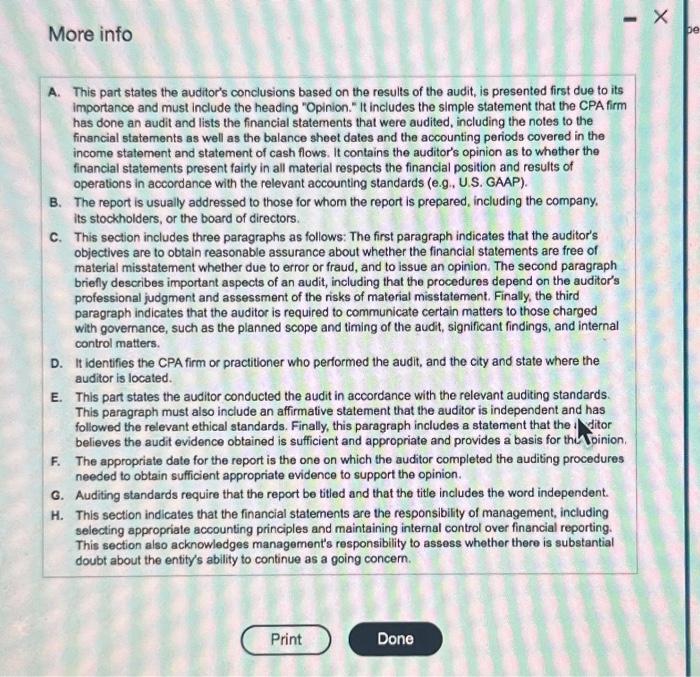
More info A. This part states the auditor's conclusions based on the results of the audit, is presented first due to its importance and must include the heading "Opinion." It includes the simple statement that the CPA firm has done an audit and lists the financial statements that were audited, including the notes to the finsncial statements as well as the balance sheet dates and the accounting periods covered in the income statement and statement of cash flows. It contains the auditor's opinion as to whether the financial statements present fairly in all material respects the financial position and results of operations in accordance with the relevant accounting standards (e.g., U.S. GAAP). B. The report is usually addressed to those for whom the report is prepared, including the company. its stockholders, or the board of directors. C. This section includes three paragraphs as follows: The first paragraph indicates that the auditor's objectives are to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement whether due to error or fraud, and to issue an opinion. The second paragraph briefly describes important aspects of an audit, including that the procedures depend on the auditor's professional judgment and assessment of the risks of material misstatement. Finally, the third paragraph indicates that the auditor is required to communicate certain matters to those charged with governance, such as the planned scope and timing of the audit, significant findings, and internal control matters. D. It identifies the CPA firm or practitioner who performed the audit, and the city and state where the auditor is located. E. This part states the auditor conducted the audit in accordance with the relevant auditing standards. This paragraph must also include an affirmative statement that the auditor is independent and has followed the relevant ethical standards. Finally, this paragraph includes a statement that the I ditor believes the audit evidence obtained is sufficient and appropriate and provides a basis for tha Doinion. F. The appropriate date for the report is the one on which the auditor completed the auditing procedures needed to obtain sufficient appropriate evidence to support the opinion. G. Auditing standards require that the report be titled and that the title includes the word independent. H. This section indicates that the financial statements are the responsibility of management, including selecting appropriate accounting principles and maintaining internal control over financial reporting. This section also acknowledges management's responsibility to assess whether there is substantial doubt about the entity's ability to continue as a going concern.
Expert Answer
In the United States, a standard unmodified opinion audit report for a nonpublic entity typically consists of eight parts. The main content provided in each part is as follows:Report Title: The title usually includes the word "Independent" to emphasize the auditor's objectivity and independence. For example, "Independent Auditor's Report."Addressee: This section specifies the intended recipient of the report, such as the entity's shareholders, board of directors, or other designated parties.Introductory Paragraph: The introductory paragraph states that the audit was conducted in accordance with generally accepted auditing standards (GAAS) and identifies the financial statements that were audited, including the specific dates or periods covered.Management's Responsibility: This part describes the management's responsibility for preparing the financial statements and maintaining adequate internal controls. It also acknowledges that the auditor's responsibility is to express an opinion on the financial statements.Auditor's Responsibility: This section outlines the auditor's responsibilities, which include planning and performing the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free from material misstatement. It also mentions that the audit involved assessing internal controls and performing procedures to obtain audit evidence.Opinion on Financial Statements: The auditor's opinion on the financial statements is presented in this part. In an unmodified opinion, the auditor expresses that the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position, results of operations, and cash flows in accordance with the applicable financial reporting framework (usually U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles or GAAP).Other Reporting Responsibilities: If applicable, this section may include additional reporting responsibilities, such as reporting on internal control over financial reporting or compliance with specific laws or regulations.Auditor's Signature, Firm Name, and Date: The report concludes with the auditor's signature, the name of the auditing firm, and the date of the report. This demonstrates the auditor's accountability for the opinion expressed and allows for identification and reference.It's important to note that while these eight parts are common in a standard unmodified opinion audit report, there can be variations based on specific reporting requirements and circumstances. Therefore, it's advisable to consult the applicable auditing standards and regulations for the most accurate and up-to-date information.